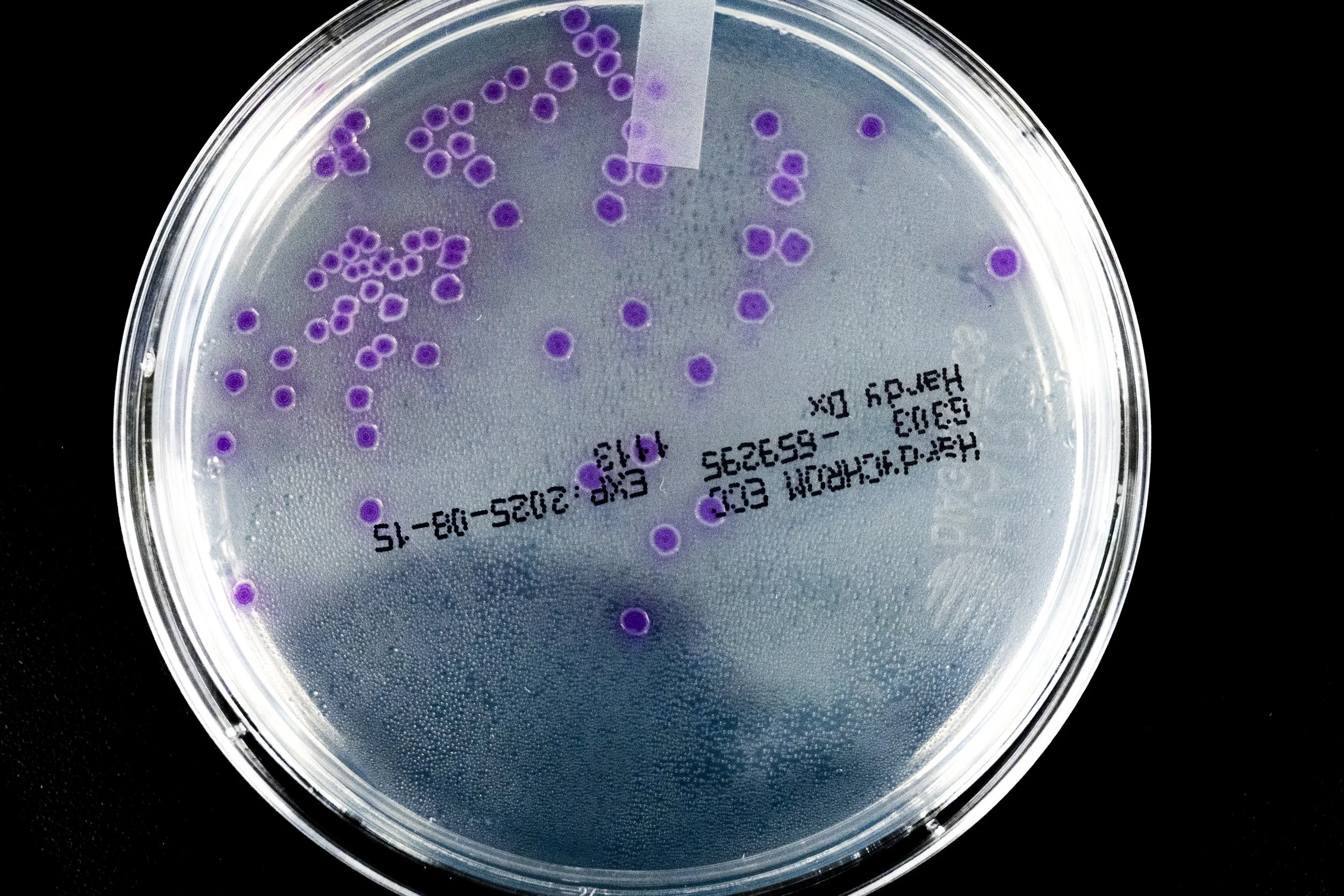
Escherichia Coli
TAXONOMY
Domain: Bacteria;
Phylum: Pseudomonadota (Proteobacteria)
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Order: Enterobacterales
Family: Enterobacteriaceae
Genus: Escherichia
MORPHOLOGY
Shape: Gram-negative rods (bacilli), typically 1–2 µm long
Gram Status: Gram-negative
Motility: Many strains are motile via peritrichous flagella; +P and 1‑type fimbriae aid attachment
Spore Formation: Non-spore-forming
Biofilm Formation: Strong biofilm producers on surfaces; fimbriae and surface factors play key roles
Other Traits: Lipopolysaccharide (LPS with O antigen), various K (capsular) antigens, and H (flagellar) antigens
NOTABLE TRAITS
Environmental/Food Safety: Widely found in intestines of warm-blooded animals; indicator of fecal contamination; thrives in varied environments Wikipedia
Virulence Factors:
Fimbriae and pili: type 1 fimbriae, P-pili (uropathogenic), F1C, S-pili
Toxins: Shiga toxins (Stx1/2) in EHEC/STEC, heat-labile/stable toxins in ETEC, hemolysin in UPEC
Iron acquisition & others: siderophores, adhesins, flagella
Survival Tolerance: Adapts to various pH, temperature; survives in food/water environments